|
ECHONOMY
Tools for Echocardiographic Calculations
Muhamed Saric, MD, PhD
New York University
|
|
 |
Diagnosis of Intra-LV Delay (LV Dyssynchrony)
|
Normal Intra-LV Delay:
Normally, LV contraction starts in the interventricular septum and spreads
throughout the LV within 40 msec.
Mechanical Intra-LV Delay:
Mechanical dyssynchrony is usually associated with prolonged QRS on surface
EKG and is typically seen with left bundle branch block (LBBB). LV
contraction starts in the region of interventricular septum and the anterior
wall. It then progresses in a delayed fashion toward the
infero-postero-lateral LV segments.
Diagnosis of Intra-LV Delay by Echocardiography:
Multiple echocardiographic techniques are used; most data exist for
color tissue Doppler-based techniques.
|
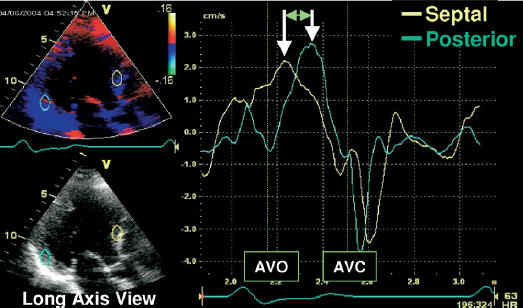
Intra-LV Delay: Color Tissue Doppler Method
|
Among all methods, this is the preferred
method.
- Obtain color tissue Doppler curves in apical views (A4C, A2C and A3C)
during a breath hold.
- Measure the opposing wall
delay using the
peak-to-peak time distance between S waves:
: A4C - inferior septum to lateral wall
: A2C - anterior wall to inferior wall
: A3C - anterior wall to inferolateral (posterior) wall.
- Report the largest opposing wall delay.
: Abnormal opposing wall delay by
color tissue Doppler >65 msec.
Caveat: No guidelines exist for the use of opposing wall technique
in atrial fibrillation.
Source: J Am Soc
Echocardiogr.
2008 Mar;21(3):191-213.
|
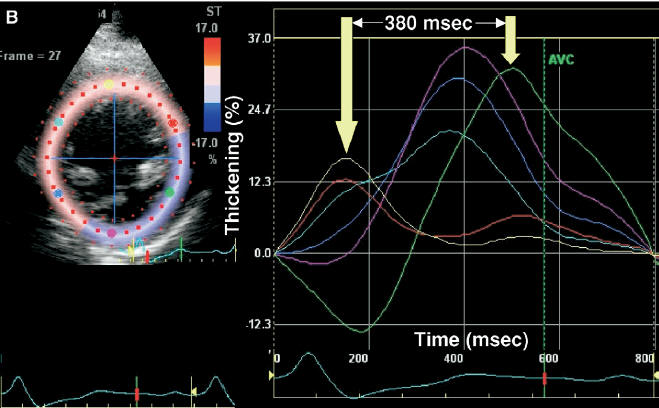
Intra-LV Delay: LV Strain Methods
|
Of all strain methods,
speckle tracking radial strain
is the preferred method at present.
- Obtain radial strain curves in the
short axis view at the level of
papillary muscles.
- Measure the time difference between peak stain values in opposing
walls (septum vs. posterior walls)
: Abnormal opposing wall delay by
radial strain >130
msec
 Source:
J Am Soc Echocardiogr.
2008
Mar;21(3):191-213.
|
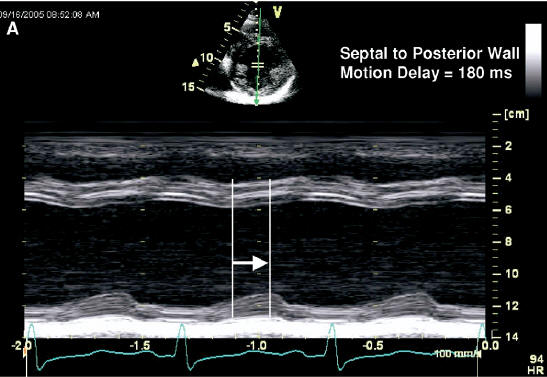
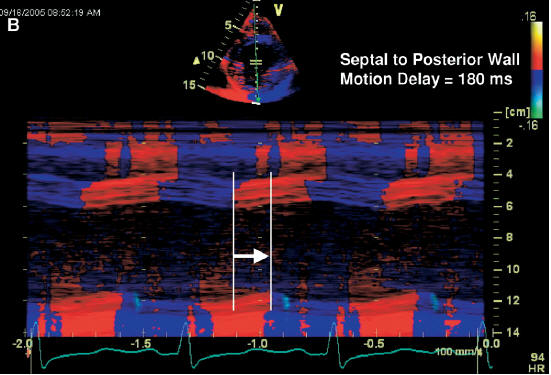
Intra-LV Delay: M Mode Methods
|
Of all the methods, M mode techniques are least
reliable and should be used only to supplement other techniques.
- Obtain the parasternal
long-axis or short-axis view of the left ventricle in standard or
color M mode.
- Measure the opposing wall (septum to posterior wall) delay:
: Abnormal opposing wall delay by
M mode >130
msec
  Source:
J Am Soc Echocardiogr.
2008
Mar;21(3):191-213.
|
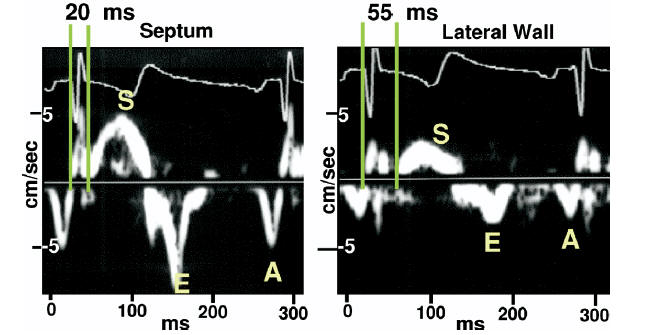
Intra-LV Delay: Spectral Doppler Methods
|
Compared to color Doppler methods:
 | There are much less data for spectral Doppler techniques |
 | In spectral Doppler techniques
time to onset of S wave rather than time to peak S wave is used.
: Abnormal opposing wall delay of
spectral Doppler - Not well defined. |
Source:
J Am Soc Echocardiogr.
2008
Mar;21(3):191-213.
|
Intra-LV Delay: 3D Echo Method
|
Compared to color Doppler methods:
 | 3D echo methods for intra-LV are less established
|
- Obtained a full 3D volume of LV
- Use 3DQ Advanced in QLab package
- Display time-LV volume curves
- Obtain the systolic
dyssynchrony index (SDI) defined as the SD of time to minimum
systolic volume of the 16 LV segments, expressed in percent RR duration.
: Abnormal SDI of 3D echo > 8%
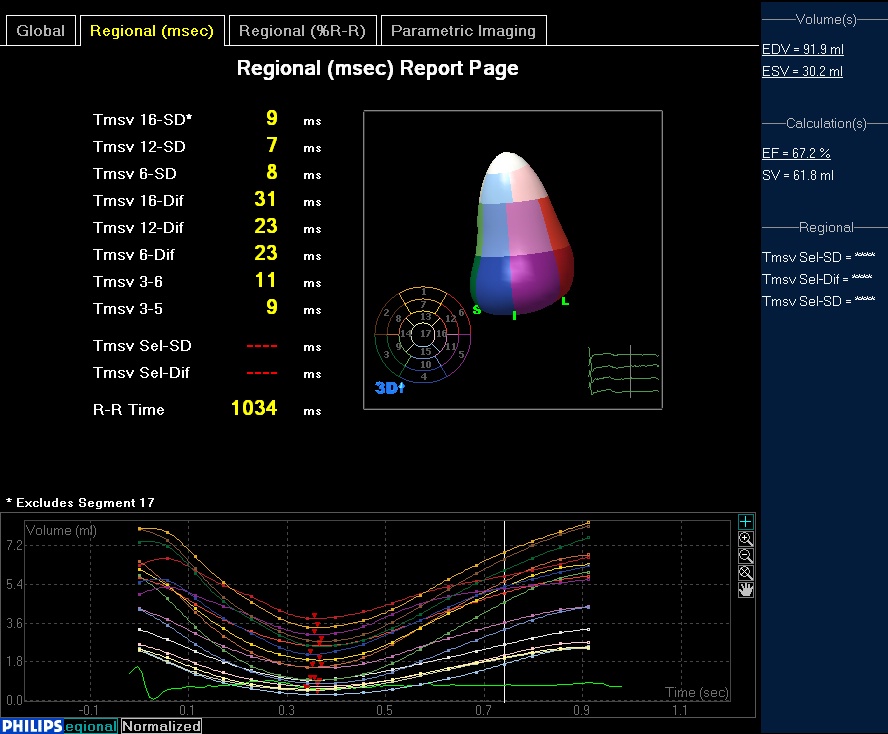
3D echo data from a patient without LV dyssynchrony |
Pacemaker Optimization of Intra-LV Delay
|
 |
Once the biventricular pacemaker is implanted, no intra-LV
optimization is feasible. |
 |
All intra-LV optimization should occur prior to
biventricular pacemaker implantation. |
 |
Echocadiography may be used to guide the optimal placement
of the LV pacing lead. |
|
Reference
|
| Gorcsan J 3rd, Abraham T, Agler DA, Bax JJ,
Derumeaux G, Grimm RA, Martin R, Steinberg JS, Sutton MS, Yu CM; American
Society of Echocardiography Dyssynchrony Writing Group.
Echocardiography for cardiac resynchronization therapy: recommendations for
performance and reporting--a report from the American Society of
Echocardiography Dyssynchrony Writing Group endorsed by the Heart Rhythm
Society. J Am Soc
Echocardiogr. 2008 Mar;21(3):191-213. Soliman OI, Geleijnse ML,
Theuns DA, van Dalen BM, Vletter WB, Jordaens LJ, Metawei AK, Al-Amin AM,
ten Cate FJ. Usefulness of left ventricular systolic dyssynchrony by
real-time three-dimensional echocardiography to predict long-term response
to cardiac resynchronization therapy.
Am J Cardiol.
2009 Jun 1;103(11):1586-91. Epub 2009 Apr 8. |
| |